The data fabric offers a modern, streamlined way to integrate data in complex environments. Learn how to take advantage of it.
In the digital age of 2025, companies generate and manage unprecedented volumes of data. According to Forbes, the total volume of data globally will grow from 64.2 zettabytes in 2020 to approximately 181 zettabytes in 2025.
This explosion and information is driving the need for modern data management and 2025 data integration solutions capable of unifying data dispersed across multiple systems, platforms and geographies.
Emerging modern data architecture concepts such as data fabric and data mesh have become fundamental to achieving enterprise data unification in complex environments. In particular, the data fabric stands out as the key to integrating heterogeneous data sources and providing agile, centralized access to enterprise data.
However, data alone is worthless if it is not converted into knowledge for the business. Therefore, data management must go hand in hand with knowledge management, ensuring that integrated information is transformed into useful insights for decision making.
More and more organizations - especiallymultinationals with distributed infrastructures -are adopting flexible data architectures to stay competitive. In this context, data fabric (often translated as "data fabric") offers a unified approach to large-scale data integration and management.
Below, we explore how a data fabric works and the main benefits it brings to enterprises with heterogeneous data, such as centralized access to information and reduction of data silos.
Want to master modern data management?
Download our free guide and learn how to design a robust, efficient data architecture tailored to your organization’s needs.
What Is a Data Fabric?
A data fabric is an intelligent data architecture that connects distributed data across multiple environments without moving it, enabling unified, secure, and automated access.
How Does a Data Fabric Work?
In essence, a data fabric acts as a layer or "fabric" that allows data to be accessed wherever it is (on-premises, in multiple clouds, or in edge environments) in a way that is transparent to the user.
Thanks to this distributed architecture, end users can view and leverage data in a unified way, even though it physically resides on different systems.
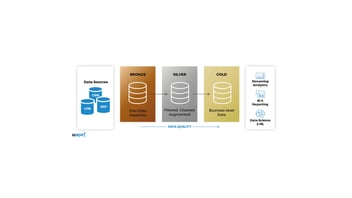
The following Gartner diagram illustrates how a data fabric works, operating as an integrating layer between various data sources (databases, data lakes, cloud stores, files, applications) and information consumers (business departments, analysts, BI tools, etc.).

In the image we see how the data fabric "weaves" a network over the various data silos, delivering integrated data to whoever needs it.
Key components of a Data Fabric architecture
- Distributed architecture and data virtualization: A data fabric is based on a distributed data architecture that spans on-premises systems, public/private clouds and even IoT devices. It uses data virtualization techniques to centralize access to multiple sources without replacing existing technologies. This allows querying and combining data from multiple sources in real time, without physically moving or duplicating them.
- Intensive use of metadata: The data fabric builds a complete map of the organization's data using rich metadata. Each data source, table, file or stream has descriptive information associated with it (location, schema, format, relationships with other data, quality, etc.). This active metadata feeds intelligent data catalogs that make it easier to find and understand the available information.
- Automation of data processes: Much of the integration and management within a data fabric is automated. For example, when a new data source emerges, the system can automatically catalog it, apply quality rules, and prepare it for use. Data process automation reduces manual intervention in repetitive tasks (ingestion, cleansing, transformation), speeding up data integration projects.
- Artificial intelligence in data integration: A key aspect of modern data fabric architectures is the use of artificial intelligence in data integration. Machine learning algorithms analyze metadata and usage patterns to recommend joins between data sets, detect inconsistencies or even suggest improvements in data structure. This AI layer enables more intelligent and adaptive integration. In fact, many data fabric solutions incorporate AI-augmented data governance capabilities (i.e., data governance with artificial intelligence), making it easier to proactively maintain data quality and security.
- Integrated governance and security: A data fabric integrates data governance mechanisms throughout the platform. This means that security, privacy, quality and compliance policies are applied uniformly across all connected data sources. By having a global view of data, it is easier to control who accesses what information, track data lineage and ensure compliance with regulations (e.g. GDPR). Integrated governance not only protects sensitive information, but also ensures that data is trusted and aligned with common definitions across the enterprise. This approach aligns with automated data governance trends, where many policies and validations are applied automatically to reduce manual intervention.
Improve data management in your enterprise Learn how to unify, protect and automate your data with a strategic data
|
Data Fabric or Data Mesh? Differences and Complementary Approaches
As we have already seen, thedata fabric acts as an intelligent layer that unifies, automates and governs the flow of data in an organization. Unlike a data mesh, which emphasizes decentralization and domain-based data management, the data fabric offers a centralized approach to access and control, relying on metadata and automation to simplify complexity.
The two approaches are not mutually exclusive, but complementary within a modern data architecture: while the data mesh distributes responsibility to each business domain, the data fabric provides the technological "backbone" that connects those domains, offering a unified experience to data users.
Benefits for Multinational and Heterogeneous Data Enterprises
For large or international companies, whose data is often spread across multiple subsidiaries, departments and disparate systems, adopting a data fabric is a quantum leap in data management. Here are two key benefits that this approach brings to organizations with heterogeneous data environments:
1. Centralized, Seamless Access to Data
One of the main benefits of a data fabric is that it provides unified enterprise data access, eliminating barriers between systems.
Instead of having to consult multiple separate databases or applications, users have a centralized point from which they can seamlessly access company-wide information.
This means that managers, analysts and employees from different areas work with consistent, up-to-date data, no matter where it comes from. In fact, by consolidating data through a data fabric, the entire company operates on the same "single source of truth" in terms of data, avoiding discrepancies between departments.
This centralized access significantly improves decision-making agility. By having a complete, near real-time view of the business, companies can spot opportunities or problems more quickly. For example, a manager could consult in minutes indicators that previously required hours or days of manual compilation in different systems.
In addition, advanced data analytics is most effective when applied to a unified, well-governed data set.
In practice, many organizations have already begun to centralize their data using cloud platforms such as Snowflake, which allow data from a variety of sources to be integrated in one place.
A data fabric approach takes this concept a step further: it not only centralizes the query, but also virtualizes and unifies access even without the need to physically migrate all data to a single repository.
Thus, a balance is struck between logical centralization and the technical flexibility of keeping each system in its optimal place. The result is a much more agile, consistent and accessible access to information for those who need it, increasing productivity and facilitating data management at the corporate level.
2. Reducing Information Silos
Another crucial benefit of the data fabric approach is the reduction of information silos.
In many companies, each department or subsidiary stores its data separately (in different applications, spreadsheets, local databases, etc.), creating disconnected islands of information.
These data silos cause inefficiencies: they make it difficult to obtain a global view of the business, duplicate integration efforts and can lead to conflicting versions of "reality" (each area with its own numbers).
A data fabric breaks down these barriers by interconnecting all data, allowing it to flow through the organization. Rather than trying to replace or dismantle each legacy system, the data fabric functions as a unifying layer that "knits together" the dispersed information and makes it usable at a global level.
By eliminating many of these silos, efficiency is improved and cross-departmental collaboration is fostered. Teams can access data from other areas in a controlled manner, which facilitates cross-functional projects (for example, a marketing campaign can combine data from sales, finance and production for a 360° picture). This not only streamlines work, but also promotes a culture of decision-making based on shared data rather than isolated intuitions.
3. Data Governance
Reducing information silos also simplifies data governance.
In a fragmented environment, each silo could have different security and quality policies, making it difficult to comply with corporate standards and regulations.
With a data fabric, governance is applied centrally and consistently across all data. Access, privacy (e.g., anonymization of personal data) and quality rules are managed from a single point, reducing risks and duplicated efforts. In fact, by unifying management, it is easier to ensure the integrity and reliability of information across the company.
The IT team can establish uniform controls and have full data traceability (knowing where each piece of data came from and who used it), reinforcing both trust in the information and regulatory compliance.
In short, a data fabric turns a siloed organization into a data-connected organization. This translates into greater operational efficiency, better collective decision making and a solid foundation for innovation and digital transformation initiatives, by having integrated and comprehensively governed data.
Conclusion
As we have seen, a well-implemented data fabric can be the key for enterprises to meet the challenges of data integration in 2025 and beyond.
However, achieving its benefits requires more than just technological tools: it requires strategic vision, cultural changes and careful planning.
In fact, the implementation of this architecture must be supported by a solid data management plan that defines clear processes, responsibilities and objectives.
Having a structured data management plan (Data Management Plan) and good governance from the outset is essential to ensure the success of a data fabric project.
In short, the data fabric is emerging as one of the most powerful modern data integration solutions to break down silos and accelerate business innovation. Business managers and decision makers have the opportunity to transform their organizations into true data-driven enterprises by leveraging data fabric infrastructure for unified, reliable, real-time insights.
Take the next step in your data strategy!
Access our practical guide to designing modern data management with governance, automation, and strategic insight.