Learn about the 5 trends in data integration for 2025: real-time, no-code, AI, hybrid ETL-ELT and Zero-ETL models to scale your data-driven strategy.
Data integration has evolved from a secondary technical task to become, by 2025, the strategic engine powering artificial intelligence, real-time personalization, and data-driven decision-making.
In an environment where data volumes are growing relentlessly and latency is no longer tolerable, traditional ETL architectures fall short of today’s demands. In their place, more agile, automated, and cloud-native approaches are taking center stage.
From streaming integration and AI-powered ETL to hybrid ETL-ELT models and disruptive innovations like Zero-ETL, organizations are reengineering their data pipelines to keep pace with modern business needs.
This article explores the five key trends in data integration that are shaping the near future—focusing on real-world use cases, leading tools, and the competitive advantages they offer to modern data teams.
At Bismart, we are experts in data integration. For years, we’ve been helping organizations across all industries connect their systems, automate processes, consolidate information, and ensure interoperability across platforms.
We offer our own data integration solution that enables companies to standardize and streamline the capture, loading, and transformation of data efficiently—minimizing the impact on business operations and ensuring business continuity.
We work with a wide range of technologies and integration scenarios, adapting to each organization's specific needs. Our business-first approach delivers flexibility, scalability, and fast implementation to drive better data outcomes.
5 Key Trends in Data Integration 2025
1. Real-Time Data Integration

Real-time data integration has become a strategic priority for data-driven enterprises. Unlike traditional batch processing, this approach enables data to be captured, processed, and unified the moment it is generated—with minimal latency, often just a few milliseconds.
This paradigm allows companies to operate at the speed of business, detect anomalies as they happen, and make timely, informed decisions.
Moreover, real-time data integration now serves as the technological backbone for generative AI, hyper-personalization, intelligent automation, and other advanced capabilities that require instant, continuous access to fresh data.
Guide: Best Practices for Data Integration
In our free ebook, “11 Best Practices for Optimizing Your Data Integration Processes,” you'll find expert advice and best practices for efficient and productive data integration.
What is real-time data integration?
Real-time data integration is a technique that enables data to be processed and synchronized the moment it is generated—without waiting for scheduled batch cycles. This approach delivers instant visibility into critical events and empowers organizations to respond at the speed of business.
Why is real-time data integration a growing trend?
It's no secret that organizations are managing unprecedented volumes of data. In fact, estimates suggest that the global data sphere will surpass 393 zettabytes by 2028, creating immense challenges around processing speed, data availability, data quality and data governance.
In this landscape, real-time data integration delivers key advantages:
- Reduced latency: enabling faster, better-informed decisions.
- Instant response to critical events: helping prevent fraud, system failures, and security threats.
- Support for AI and machine learning models: enabling real-time analysis of massive data streams.
- Enhanced customer experience: driving contextual, predictive personalization.
Despite these clear benefits, only 16% of technology leaders say their systems are prepared to support real-time genAI workloads. This highlights a pressing need to adopt agile, scalable, and cloud-native data architectures.
Are your data integration processes still isolated, non-standardized, and difficult to manage? If so, you're likely facing inefficiencies that limit your ability to scale and respond in real time.
Are your data integration processes still isolated, non-standardized, and difficult to manage? If so, you're likely facing inefficiencies that limit your ability to scale and respond in real time.
Real-Time Data Types: Streaming and Events
Real-time data integration relies on two primary types of data streams:
Streaming Data
Streaming data consists of continuous flows of information generated and transmitted in real time from various sources—such as IoT sensors, mobile apps, e-commerce platforms, social networks, or financial systems. Rather than waiting for data to accumulate, streaming data is processed as it’s produced.
This type of data is essential for use cases like:
- Instant personalized recommendations
- Real-time fraud detection
- Predictive maintenance for machinery or vehicles
- Behavioral analytics on websites or mobile apps
Event Streams
An event represents a discrete but meaningful action—such as a purchase, a click, a security alert, or a stock update. Event streams allow these actions to be processed the moment they occur, and in the precise order they happen.
This enables systems to respond immediately. For example:
- Trigger a personalized offer after a user click
- Block a suspicious transaction in real time
- Activate an alert on a monitoring dashboard
Real-Time Data Integration: Use Cases
Real-time data integration is already delivering tangible value across a wide range of industries:
- Critical systems monitoring: Immediate detection of anomalies in IT infrastructure and industrial equipment.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Seamless integration of data from sensors, connected machines, and medical devices.
- Financial services and banking: Real-time fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and dynamic risk scoring.
- Logistics and supply chain: Live tracking, adaptive route optimization, and inventory management.
- Retail, marketing, and customer experience: Hyper-personalization based on real-time behavior, context, and user preferences.
In all these scenarios, access to contextual, real-time data is what empowers organizations to shift from reactive decision-making to strategic innovation.
2. No-Code and Low-Code ETL
In a landscape where more and more business users—often without advanced IT or data skills—need to work with data, no-code ETL tools and low-code data integration platforms have emerged as essential solutions.
These technologies enable users to design and automate visual data pipelines without writing code, making data more accessible to non-technical teams and reducing reliance on specialized data engineering resources.
What is No-Code ETL?
No-Code ETL is a method of extracting, transforming, and loading data using drag-and-drop visual interfaces—without writing a single line of code.
It is especially useful for:
- Non-technical users in marketing, finance, operations, and other business functions
- Small to mid-sized teams without dedicated data engineers
- Repetitive or standard integrations between widely used platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, Shopify, BigQuery, or Snowflake
Through guided, intuitive workflows, users can:
- Connect systems using prebuilt connectors
- Automate basic transformations with visual tools
- Send data to warehouses, spreadsheets, or dashboards in just minutes
By eliminating manual exports and reducing human error, no-code ETL tools empower business users to accelerate data-driven decision-making without depending on IT teams.
Key Benefits of No-Code ETL
- Full accessibility: Empower any user—regardless of technical background—to build and manage data pipelines.
- Faster operations: Set up and deploy data streams in just minutes, accelerating time to insight.
- Reduced technical dependency: No SQL or coding skills required, freeing up data engineering resources.
- Break down data silos: Enable cross-departmental access to consistent, synchronized data.
- Scalable automation: Configure flows to run automatically, ensuring efficiency and repeatability at scale.
What is Low-Code ETL?
Unlike the no-code approach, low-code ETL strikes a balance between ease of use and technical flexibility. It enables users to automate complex data pipelines through visual interfaces while allowing the inclusion of custom code snippets—such as SQL, Python, or shell scripts—for advanced logic and control.
Low-code ETL is ideal for:
- Data analysts and engineers who require customization without building everything from the ground up
- Custom integrations that go beyond the limitations of standard connectors
- Hybrid environments (cloud + on-premises) with complex rules or irregular data structures
With a low-code approach, you can:
- Process larger data volumes efficiently
- Apply specific transformations without full-scale development
- Boost technical team productivity by reusing visual components and configurable modules
In short, low-code ETL empowers teams to build scalable, customizable, and business-specific data flows faster and with less effort.
Why Are They a Game-Changer for Business Teams?
No-code and low-code ETL tools are transforming how organizations access, transform, and activate their data.
According to recent research, companies that adopt no-code or low-code integration tools can reduce integration design and development time by up to 80% compared to traditional ETL methods.
The key strategic advantages include:
- Faster response times: Enabling near-instant analysis of new business challenges
- Operational agility: Allowing teams to automate their own processes without delays
- Reduced dependency on IT: Freeing up technical staff to focus on high-impact, strategic initiatives
- Improved data utilization: Eliminating barriers to information access and reducing friction
No-code and low-code platforms empower “citizen integrators”—business users with technical autonomy—to connect, move, and transform data independently, without creating silos or relying heavily on engineering teams.
Additionally, these tools are highly compatible with modern initiatives such as real-time data integration, self-service BI, and AI-driven business automation.
3. AI-powered ETL
The growing complexity of data, the diversity of formats, and the demand for real-time insights have accelerated the evolution of traditional ETL processes.
By 2025, AI-powered ETL has emerged as one of the most effective solutions for automating, optimizing, and scaling data integration.
This new approach transforms ETL into an intelligent system, capable of detecting anomalies, adapting to evolving data schemas, and performing complex transformations with minimal human intervention.
By leveraging machine learning and predictive capabilities, organizations can achieve more agile, accurate, and cost-efficient data integration at scale.
What is AI-powered ETL?
AI-powered ETL leverages machine learning algorithms to automate the extraction, transformation, and loading of data. It adapts to changing data structures, automatically detects errors, and optimizes data pipelines, minimizing the need for manual intervention.
Unlike traditional ETL processes, which rely on static scripts and predefined workflows, intelligent ETL powered by AI introduces key innovations:
- Automation of complex tasks: from field mapping to data normalization
- Dynamic adaptability: pipelines automatically adjust to schema changes and new data sources
- Real-time error detection: AI identifies and resolves data inconsistencies proactively
- Reduced time and costs: repetitive tasks are eliminated, accelerating time-to-insight
Recent studies show that automating ETL pipelines with AI significantly reduces manual workload and can increase operational productivity for data teams by up to 150%.
How Artificial Intelligence Enhances Every Stage of the ETL Process
Intelligent Data Extraction
- Automatic detection and connection to APIs, databases, cloud services, and unstructured data sources
- Proactive identification of incompatible formats, missing fields, and structural anomalies
Machine Learning–Driven Data Transformation
- Data cleaning, standardization, and enrichment using models trained on historical patterns
- Ability to process unstructured data (e.g., text, images) and convert it into usable, analyzable information
Optimized Loading into Analytical Destinations
- Analysis of usage patterns to determine the most efficient loading strategies
- Use of advanced techniques such as dynamic compression, adaptive indexing, and intelligent load balancing to maximize performance and scalability
Key functionalities of ETL with AI automation
The most advanced AI-driven ETL platforms combine multiple capabilities to streamline and enhance data integration processes:
- Auto-mapping and schema drift detection: Automatically identifies changes in data structure—no manual updates required
- Intelligent Change Data Capture (CDC): Real-time synchronization of data changes with built-in error resilience
- Automated profiling and normalization: Enhances data quality by detecting inconsistencies and standardizing formats
- Built-in anonymization and encryption: Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA
- Predictive load optimization and parallel processing: Increases performance and scalability across large datasets
- AI-based monitoring and observability: Includes root cause analysis, automatic recovery, proactive alerts, and detailed logging
The Best ETL Tools with AI in 2025
| Platform | Featured AI capabilities | Real-time support | Technical focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrate.io | Anomaly detection with LLMs, GPU pipelines, auto-schematics | ✅ CDC | Low-code / visual |
| Fivetran | Automatic schema evolution, integration with GenAI | ✅ | External via dbt |
| Airbyte | IA Assist, automatic connector generator | ✅ CDC | Code (Java/Python) |
| SnapLogic | SnapGPT, vector search, agent creation. | ✅ | Visual / low-code |
| Talend | Profiling and governance with AI, data quality | ⚠️ Limited | GUI + scripting |
| Informatics | CLAIRE AI engine, AI co-pilots, GenAI recipes | ✅ | Visual + scripting |
| AWS Glue | Transformations with ML, schema inference. | ✅ | Code (Python/Scala) |
- Don't miss: How to choose the right ETL tool?
Advantages of automated ETL with AI
- Faster processing thanks to pattern recognition and parallel execution.
- Increased accuracy and data quality by identifying and correcting errors before they propagate.
- Reduced operational costs by minimizing manual tasks and technical support.
- Real-time adaptability to changes in sources, formats or volume.
- Self-repairing pipelines capable of restarting failed executions, detecting anomalies and preventing errors.
Challenges of AI-Driven ETL That Organizations Should Consider
While the benefits of AI in ETL are significant, several challenges must be addressed:
- Limited transparency (black-box effect): Automated decisions can be difficult to trace, making it harder to understand or justify certain transformations
- Regulatory and privacy compliance: Meeting requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA demands additional oversight of automated processes
- Legacy system integration: Older architectures may need reengineering to work with AI-enabled tools
- Cloud computing costs: Running AI models can require substantial computing power, potentially increasing expenses if not properly managed
Guide: Best Practices for Data Integration
In our free ebook, “11 Best Practices for Optimizing Your Data Integration Processes,” you'll find expert advice and best practices for efficient and productive data integration.
4. ELT and Hybrid Data Integration Models

As cloud environments become the standard, the ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) model has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional ETL. At the same time, many organizations are embracing hybrid ETL-ELT approaches, combining elements of both models to maximize their respective advantages.
This strategy supports more flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient data integration, adapted to the unique requirements of each use case.
Key differences between ETL and ELT
The main difference between ETL and ELT lies in when and where data transformation takes place:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Data is transformed in an intermediate environment before being loaded into the final destination. This approach typically requires additional infrastructure (staging areas), custom scripts, and dedicated computing resources.
- ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): Data is first loaded directly into a data warehouse or data lake, and then transformed within that destination—leveraging the scalable processing power of the cloud.
Other key differences:
| Feature | ETL | ELT |
|---|---|---|
| Transformation | Before loading | Within the target (data warehouse) |
| Scalability | Limited by ETL engine | Scales with cloud data warehouse |
| Data types | Best for structured data | Supports structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. |
| Ingestion speed | Slower due to transformation step | Faster: immediate load with deferred transformation. |
| Operational costs | High infrastructure and maintenance | Simplified infrastructure, lower operating cost. |
| Governance and security | Strong control before loading | Post-load controls required, although warehouses offer robust pencils. |
Why Is ELT Gaining Traction in Cloud Environments?
The rapid adoption of platforms like Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and Azure Synapse has fueled the rise of cloud-native ELT—driven by several key advantages:
- Separation of storage and compute: Enables dynamic scaling without overprovisioning infrastructure
- Fast loading without pre-transformation: Speeds up data ingestion by deferring transformation
- Native support for semi-structured and unstructured formats: Handles JSON, Avro, Parquet, images, and more with ease
- Reduced operational complexity: Eliminates the need for external orchestration tools and supports version control directly within the data warehouse
This modern ELT approach reduces analytical latency, accelerates data exploration, and integrates seamlessly with transformation tools like dbt (data build tool)—making it a powerful option for today’s data-driven organizations.
What Is a Hybrid ETL-ELT Model?
Many organizations adopt hybrid data integration models, where ETL and ELT coexist to address different types of data workloads and business requirements:
- ETL for sensitive or highly regulated data: Pre-loading transformations ensure data quality, regulatory compliance, and anonymization, especially when handling personally identifiable information (PII).
- ELT for high-volume or less critical data: Data is loaded directly into the warehouse, enabling on-demand transformation for analytics and modeling.
Functional segmentation by use case:
- ETL → financial reporting, regulatory compliance
- ELT → advanced analytics, machine learning, data science
This hybrid approach enables organizations to balance speed, security, and scalability, tailoring the integration strategy to the specific needs of each use case.
Advantages of the ELT and hybrid approach.
Key benefits of ELT
- Immediate loading and flexible processing
- Cloud resource optimization
- Reusable transformations within the warehouse
- Analytical agility and faster access to raw data
Benefits of the hybrid ETL-ELT model
- Granular control over data governance
- Reduced exposure of sensitive information
- Support for multiple source and target types
- Organizational adaptability according to priorities and regulation
Challenges and Limitations of ELT and Hybrid Models
While ELT and hybrid ETL-ELT approaches offer significant advantages, they also come with specific challenges that organizations must address:
- Data swamps: Loading raw data without governance or clear policies can lead to disorganized, unmanageable data lakes.
- Post-load security: Sensitive data requires robust access controls, masking, and audit trails within the data warehouse—after ingestion.
- Higher storage costs: Unfiltered or poorly transformed data can consume excessive storage, driving up operational costs.
- Cloud dependency: ELT relies on high-performance, cloud-native data warehouses with separated storage and compute, which may be incompatible with legacy or on-premise systems.
The ELT approach and hybrid models represent the natural evolution of modern data pipelines, enabling organizations to build flexible, scalable, and efficient data environments.
With ELT, enterprises harness the scalability of the cloud, reduce latency, and maintain analytical agility. Meanwhile, hybrid models allow for greater control, data quality, and regulatory compliance when needed.
Adopting this strategy requires a strategic shift toward more dynamic, future-ready data capabilities—built to support both operational resilience and innovation.
5. Zero-ETL: The End of an Era?
The concept of Zero-ETL is reshaping the future of data management by moving beyond traditional extract, transform, and load workflows.
Unlike conventional ETL models, Zero-ETL eliminates intermediate pipelines, enabling direct integration between source systems and analytical destinations.
This approach responds to the increasing demand for instant data availability in cloud environments by reducing latency, simplifying data architecture, and lowering operational overhead.
What is Zero-ETL?
Zero-ETL is a modern data integration strategy that removes the need for traditional ETL processes. Instead of extracting, transforming, and loading data through staged workflows, it replicates data directly from source systems to analytical storage in real time.
The Zero-ETL model is built on real-time data replication, with no explicit transformation or manipulation required before loading—resulting in significantly reduced latency, complexity, and maintenance effort.
Key Zero-ETL Technologies and Methods
The Zero-ETL paradigm is enabled by a set of modern technologies and techniques that eliminate the need for traditional ETL workflows:
- Real-time replication (Change Data Capture – CDC): Continuously synchronizes changes from source databases to target systems—for example, replicating updates from Amazon Aurora to Redshift in real time.
- Federated querying / Data virtualization: Enables cross-system queries without physically moving or duplicating data, providing a unified view across multiple sources.
- Event streaming: Processes data in motion using tools like Apache Kafka or Amazon Kinesis, eliminating the need for staging or intermediate storage.
- Schema-on-read: Applies the schema at the time of query rather than at data ingestion, allowing flexible handling of semi-structured formats like JSON, Avro, or Parquet.
Direct Replication–Based Architectures
Zero-ETL solutions are typically built on cloud-native infrastructures that support real-time, low-latency integration through direct data replication. These architectures often include:
- Native integrations between databases and analytical stores, such as Amazon Aurora and Redshift within the AWS ecosystem
- Intelligent Change Data Capture (CDC) systems that incrementally capture changes without impacting source system performance
- Serverless platforms that automatically scale based on demand, eliminating the need for resource overprovisioning
- Data virtualization, which enables unified querying across multiple sources without duplicating or physically replicating data
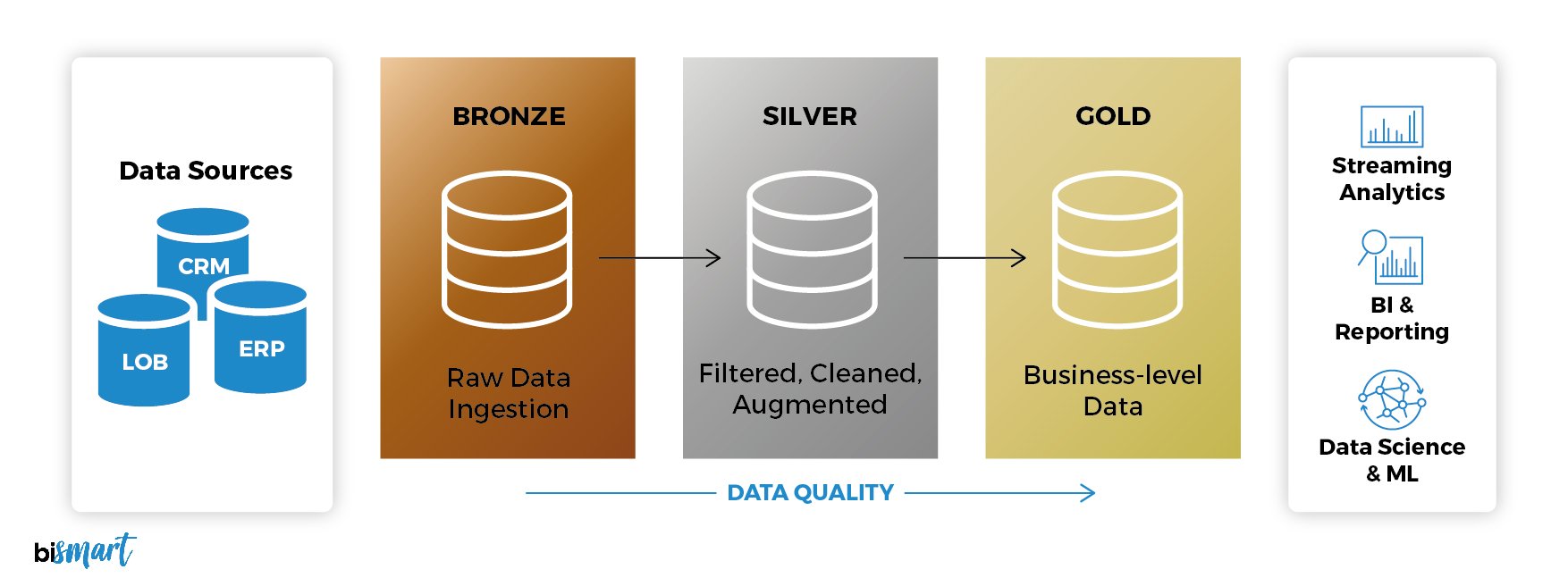
Flexible architectures like the Medallion architecture exemplify this approach—reducing technical complexity and accelerating data availability without the need to orchestrate external transformation or staging tools.
Key Advantages of the Zero-ETL Approach
Architectural Simplicity
- Eliminates the need to build and maintain complex transformation pipelines
- Reduces potential points of failure and overall operational complexity
Real-Time Data Access
- Enables near-instant synchronization from source systems
- Ideal for live dashboards, real-time alerts, and predictive analytics use cases
Lower Cost and Maintenance Effort
- No need for dedicated ETL infrastructure or third-party transformation tools
- Cuts down development time and minimizes reliance on technical support
Cloud-Native Scalability and Agility
- Seamlessly aligned with serverless platforms and multi-cloud architectures
- Facilitates rapid integration of new data sources with minimal configuration
Use Cases for the Zero-ETL Approach
- Real-time analysis of web behavior, transactional operations or business metrics.
- Direct replication from relational databases to analytical warehouses without intermediate processing.
- Federated queries between multiple sources without duplicating data.
- AI or machine learning models that require continuous data ingestion for training or inference.
Zero-ETL: Challenges and Limitations
While Zero-ETL offers significant benefits, it’s not suitable for every scenario. Key limitations include:
- Limited transformation capabilities: Without a pre-processing stage, transformation logic must be handled entirely at the destination
- Post-load governance: Requires robust data quality, security, and traceability controls within the target system
- Technology dependency: Relies on modern, cloud-native infrastructure; typically incompatible with legacy systems
- Variable cloud costs: Continuous synchronization and duplicate storage across source and destination can inflate costs if not carefully optimized
- Complex error resolution: Without a controlled intermediate layer, diagnosing issues or tracing inconsistencies becomes more challenging
Zero-ETL represents a fundamental shift in data integration strategy, moving away from traditional staging and transformation pipelines toward a model focused on direct, continuous, and flexible data access.
It is especially well-suited for organizations with data-driven strategies that prioritize speed, operational simplicity, and cloud scalability.
However, Zero-ETL is not a complete replacement for ETL or ELT. In many cases, a hybrid approach —combining Zero-ETL for real-time or operational data with traditional ETL/ELT for sensitive, complex, or heavily regulated workloads— is the most effective solution.
Ultimately, adopting a Zero-ETL model means shifting the focus from moving data to making it accessible, actionable, and auditable at the source.
Conclusion: Data Integration Is Evolving Toward Immediacy, Intelligence and Simplicity
Data integration is no longer a back-end technical task—it’s a strategic driver of innovation and competitive advantage.
By 2025, the organizations leading in real-time analytics, data-driven decision-making, and AI adoption are those embracing modern integration models such as:
- Real-time data integration
- No-code and low-code ETL
- AI-powered ETL
- Hybrid ETL/ELT frameworks
- Zero-ETL architectures
Each of these approaches addresses distinct business needs, but they all share a common goal: to deliver immediate, reliable, and governed access to data—at scale. This unlocks operational intelligence, personalization, automation, and overall business agility.
Modernizing your data pipelines by incorporating cloud-native platforms, automation, and AI isn’t just a matter of performance, it’s a fundamental shift toward faster insights, reduced complexity, and future-ready infrastructure.
📘 Download our free guide: 11 Best Practices to Optimize Your Data Integration Processes and start transforming your data architecture with the most efficient and up-to-date solutions.
Guide: Best Practices for Data Integration
In our free ebook, “11 Best Practices for Optimizing Your Data Integration Processes,” you'll find expert advice and best practices for efficient and productive data integration.