We explain the different types of machine learning and their most common practical applications. What is machine learning being used for?
Bots that seem to speak your language, cars that work without anyone behind the wheel, recommendation systems that are able to predict what you are looking for or voice assistants that understand everything you say. All of these things that seemed so far off in the future, are now possible thanks to machine learning, a type of artificial intelligence that makes machines learn. We explore the different types of machine learning that exist and their most common usages.

Jeff Hawkins, computer engineer, president of the Redwood Neuroscience Institute and founder of the companies Handspring and Palm, stated the following in the first chapter of his famous book, On Intelligence, published in 2004: "Many people today believe that AI is alive and well and just waiting for enough computing power to deliver on its many promises. When computers have sufficient memory and processing power, the thinking goes, artificial intelligence programmers will be able to make intelligent machines. I disagree. AI suffers from a fundamental flaw in that it fails to adequately address what intelligence is or what it means to understand something. A brief look at the history of AI and the tenets on which it was built will explain how the field has gone off course."
In that same book, Hawkins described human intelligence as the ability to predict the future based on prior knowledge, which is exactly what machine learning (ML) does.
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that makes machines learn by themselves based on algorithms that recognize patterns in stored information and use them to generate new information.
Machine learning algorithms make machines or computers capable of analyzing and solving problems in a similar way humans do.
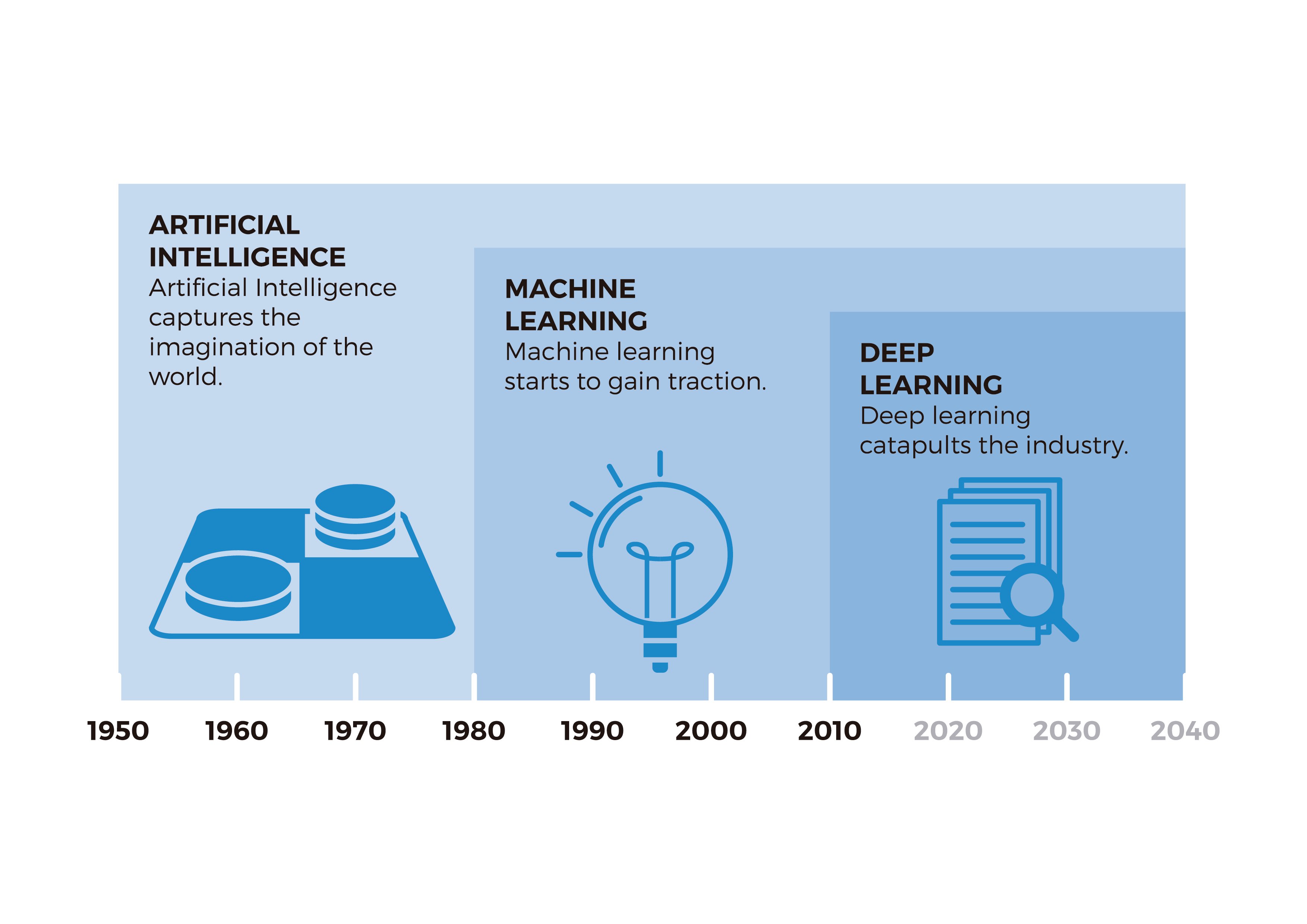
In 2010, a new field of machine learning emerged, deep learning (DL), which operates in a very similar way to machine learning, but using algorithms that are even more similar to the way human neural networks work.
Types of machine learning
Currently, there are three different types of machine learning that differ from each other by the type of algorithm they use. Supervised machine learning and unsupervised machine learning are the two most common types of machine learning, but there is a third machine learning algorithm: reinforcement machine learning.
Supervised Machine Learning
This type of machine learning works with algorithms that have the ability to "learn" from data managed by a human. In other words, supervised machine learning algorithms require the intervention of a human to classify, label and enter the data into the system in order to generate more information autonomously. From the labels applied to the data, supervised ML algorithms are able to make predictions and even complex decisions. The data entered into this type of algorithm can be either classification or regression data.
Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised machine learning algorithms operate without any human intervention and do not require prior information to "learn" or solve problems. There are two types of unsupervised machine learning algorithms: clustering algorithms and association algorithms. The purpose of unsupervised machine learning is to make the machine capable of finding patterns among disorganized and unlabeled data sets. The algorithm is in charge of finding relationships between the data to then draw its own "conclusions".
Reinforcement Machine Learning
Reinforcement machine learning algorithms are programmed to generate knowledge from previous experience. That is, this type of algorithms are able to solve problems based on the results or triggers of similar situations they have faced before.
Machine learning by reinforcement works by subjecting the machine to a series of tests in which it must make a decision. If it makes the correct decision, the system is "rewarded". After a few tests, the algorithm is able to make the correct decisions on its own.
What is machine learning being used for?
As we have already seen, artificial intelligence and machine learning are used to optimize the data-driven decision making process, as well as to generate intelligence from advanced data analytics. Other common usages are test automation, predictive analytics and process automation and optimization.
However, machine learning has practical applications in all knowledge fields and is one of the main technologies driving digital transformation and scientific advances. Let's explore some of them.
Smart cars: While we have not yet reached 'Knight Car' level, vehicles are getting smarter. Assisted driving, for example, is the result of machine learning algorithms. A recent study by IBM, Automotive 2025, suggests that, by 2025, cars will adapt automatically —radio, temperature, seating position, etc. — to the driver's preferences.
Medical research: Machine learning is one of the pillars of scientific research, especially in medicine. For example, machine learning is being used for the early detection of diseases that have a better diagnosis when detected early, such as cancer or some types of respiratory conditions.
Natural language processing (NLP): Natural language processing is one of the most frequent and useful uses of machine learning. PLN algorithms such as folksonomy are able to understand information written in natural language —the language we humans use—, to classify information and identify patterns in the data to draw conclusions. PLN is used in multiple sectors for document management and research based on large amounts of data produced in natural language. Voice assistant bots are also examples of natural language processing.
Not familiar with our PLN solution? Take a look at Folksonomy Text Analytics:
Personalization: In marketing, e-commerce and any type of business activity developed in the digital sphere, personalization is undoubtedly one of the most common applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence. Companies use machine learning algorithms for the automatic detection of behavioral patterns among consumers and use them to offer customers personalized content and, especially in e-commerce, personalized recommendations.
Search engines: Search engines also apply machine learning for content personalization. Search engines show different results to each user based on their previous searches, their online activity or demographic data such as place of residence. Try it! Tell a colleague to search for a word on Google using their phone, search for the same word and see if Google gives you the same results.
Cybersecurity: Algorithms are also applied in cybersecurity, especially for optimizing the performance of antivirus software, which, through ML algorithms, increase their ability to detect irregularities.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has evolved a lot since Hawkins wrote On Intelligence. Machine learning, deep learning and their practical applications are proof that the writer was wrong. While machines still do not have the ability to think like humans, machine learning algorithms are increasingly getting more and more similar to the human brain.